Embedded Map & Orientation
Introduce a Google Map including necessary supporting resources such as Google Play Services Library and a personal API key. Additionally, support a landscape layout, validation of geolocation input, immediate mirroring any changes in this input in the view title and support for smaller small factor devices.
Preview
Here we shall embed a Google map in the ResidenceFragment class. This entails using:
- Google Play Services Library and
- A Google API key
- Modifying the XML layout
- Adding the necessary Java code
The layout shall be refactored as shown here.
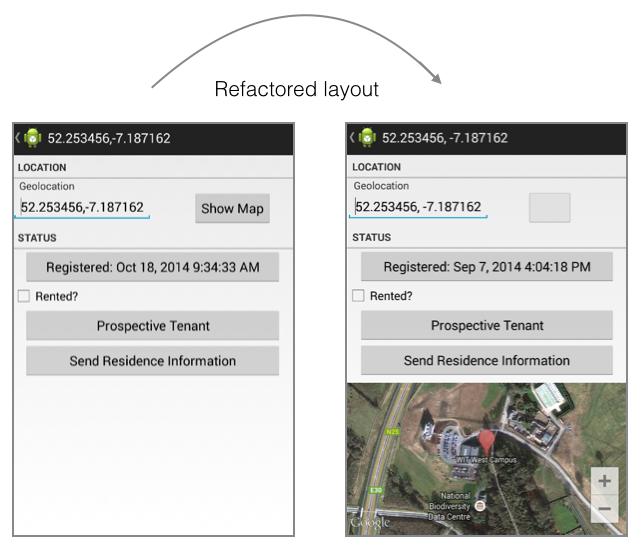
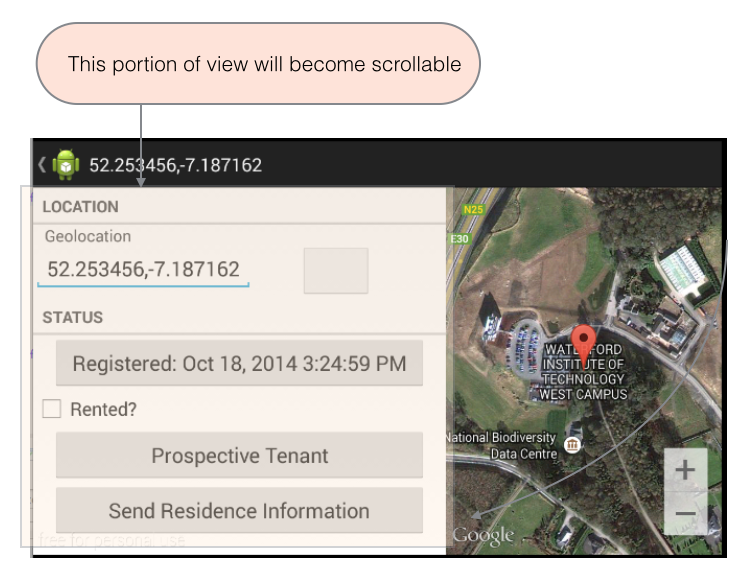
Additionally, we shall:
- Make the non-map part of the details view scrollable.
- Modify a copy of the layout suitable to display the details view in landscape mode.
The instructions in this lab refer to development in debug mode. This means that the application you develop will not be suitable to publish on Play. Further information is available about this topic is available here and here.
Google Play
It is necessary to add Google Play Services to the project.
- Launch Eclipse and open the workspace where you are developing MyRent.
-
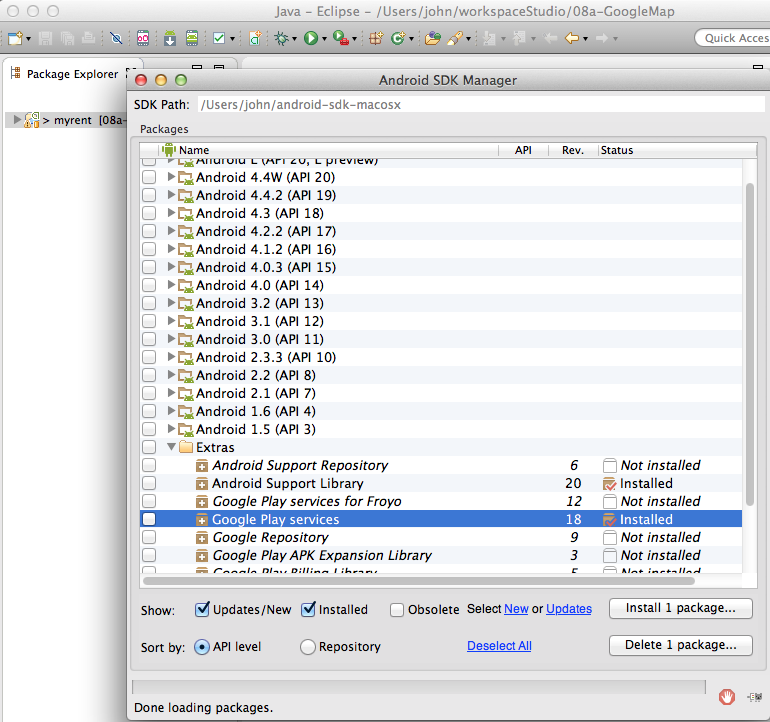
Open the Android SDK Manager and install Google Play Services:
- To do this, tick the checkbox in the Extras folder opposite Google Play Services and then press the Install Package button
-
When Play Services installation is complete select menu commands:
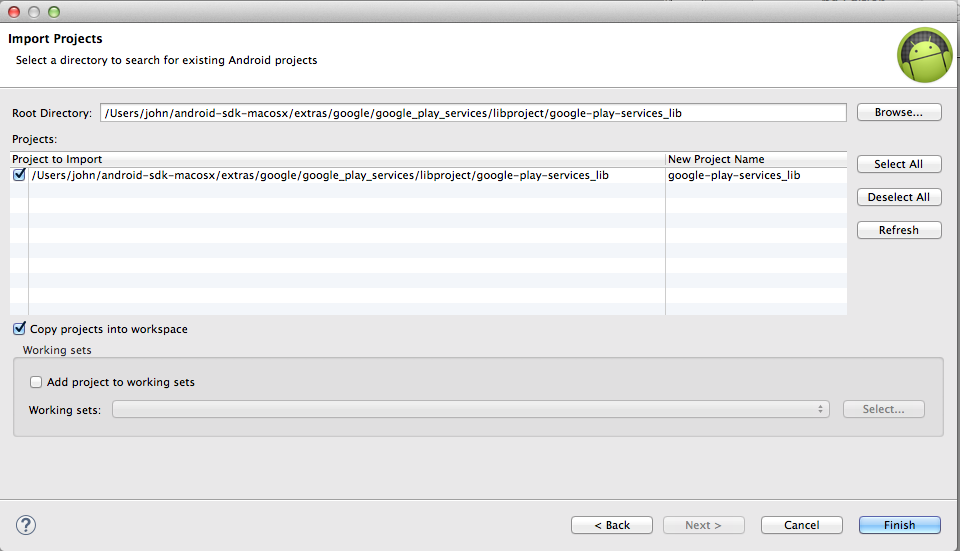
- Import | Android | Existing Android Code into Workspace:
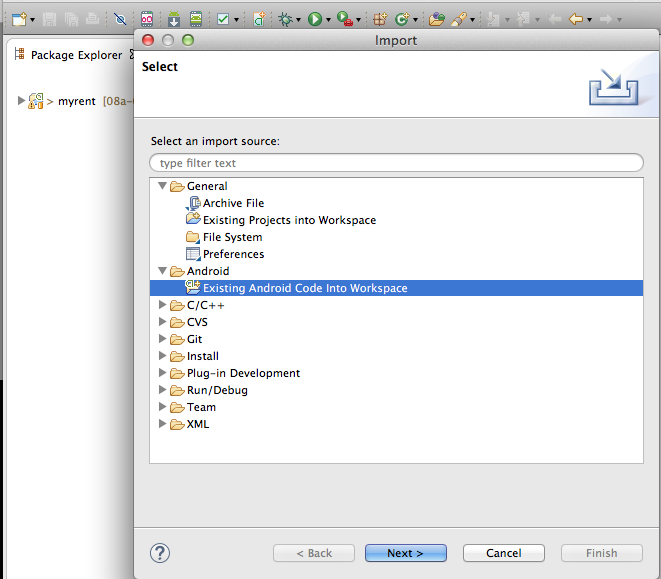
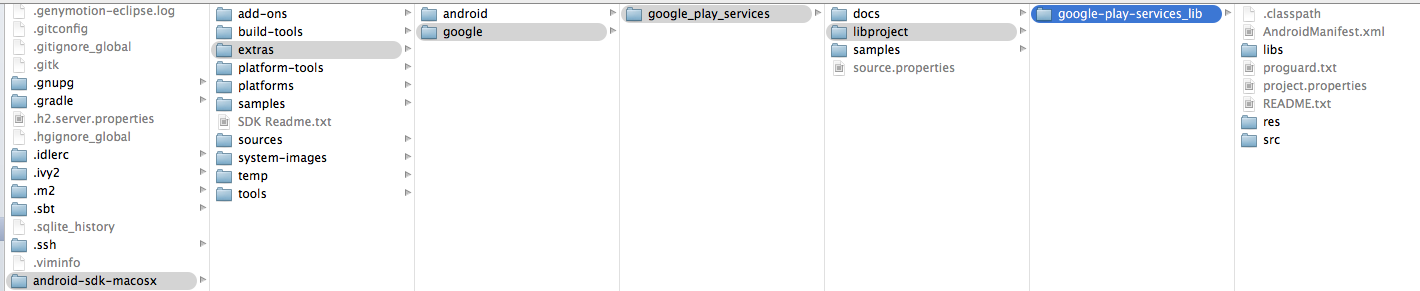
- Browse to where you have installed Android SDK and then to
- /extras/google/google_play_services/libproject/google-play-services_lib/
- Important: tick the Copy projects into workspace check box in the Import Projects window as shown in Figure 4.
- Press Finish
- Open the file google-play-services_lib/AndroidManifest.xml and change the minSdkVersion to 16 to correspond with the minimum version we are targetting in MyRent

<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="16"/>
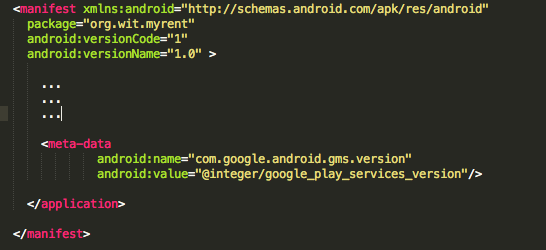
- Add the following to MyRent AndroidManifest.xml file immediately before the closing application tag (as illustrated in Figure 6):
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version"/>
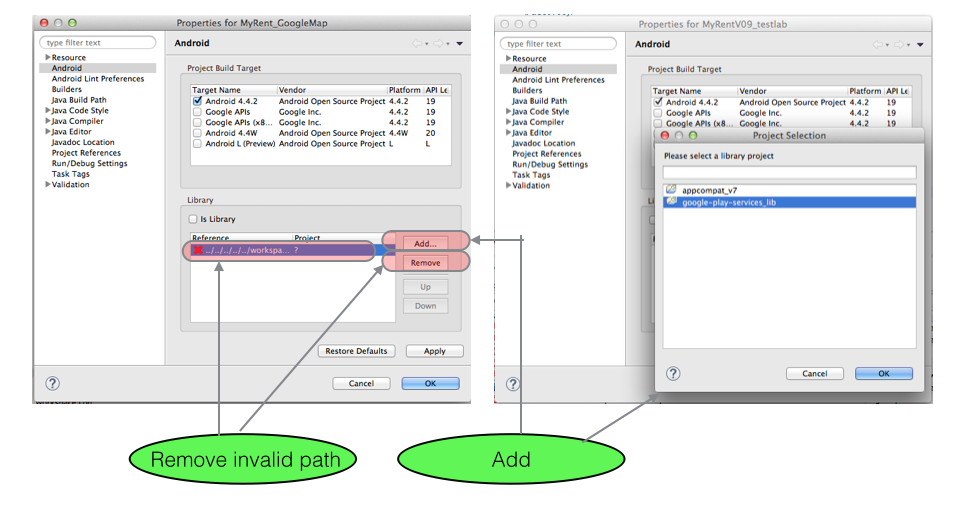
- When you have completed the above steps, reference the newly imported Play Services in MyRent project as follows:
- Highlight myrent, right click and select Properties in the context menu
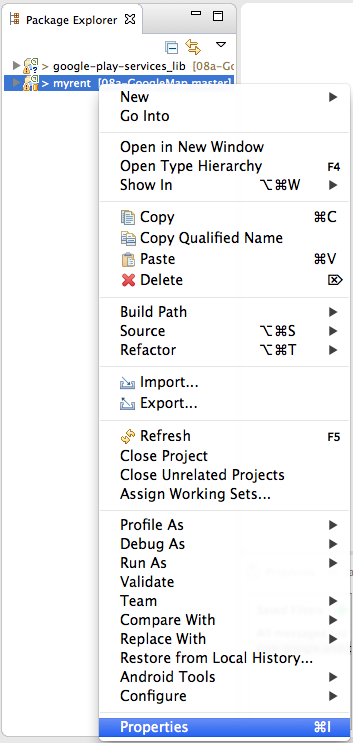
- Select google-play-services_lib in the Project Selection window and press OK
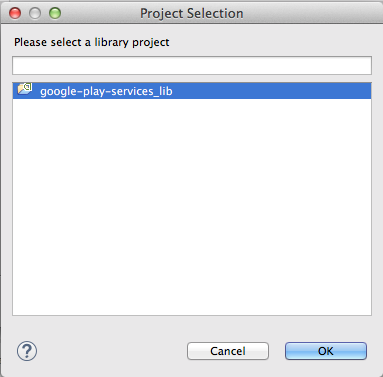
- The Properties for myrent window should now appear as shown in Figure 9.
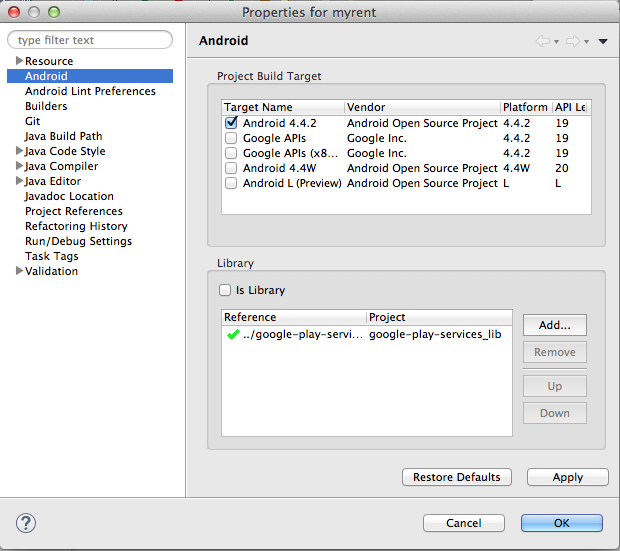
- Highlight myrent, right click and select Properties in the context menu
MyRent project has now been set up to reference Google Play Services.
Official documentation is available at the Google Maps Android API v2 page.
Important note: as an aid to portability it would help were you to locate the google-play-services_lib folder in the same containing folder as the MyRent project as shown here:

API Key
We recommend that you become familiar with the official documentation for Google Maps Android API v2.
It is necessary to obtain an API key before using the Google Maps API. This can be achieved as follows:
- You should already have imported Google Play Services to your myrent project in Eclipse.
-
Retrieve your SHA-1 Fingerprint
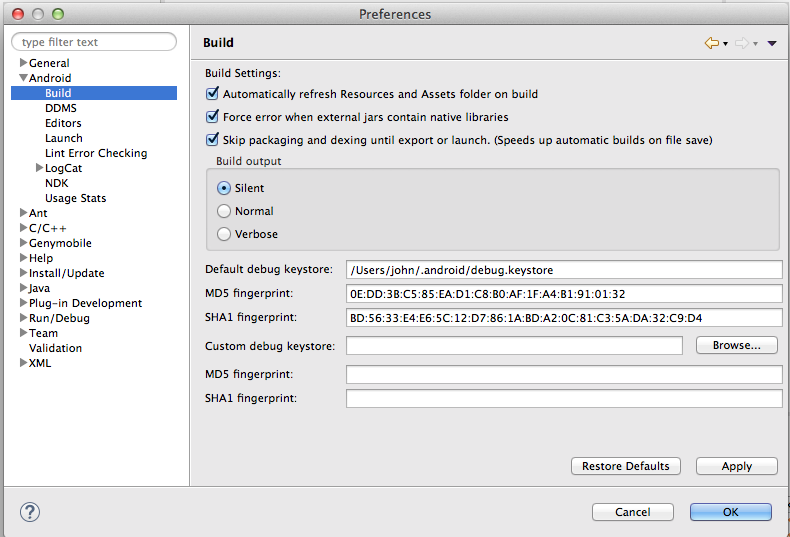
- A SHA-1 fingerprint is a unique text string required by Google Maps to identify the application.
- It can easily be obtained by opening the Preferences window and copying it from there to the required destination (see Figure 1).
- The destination for the fingerprint will be described below. In the meantime copy the fingerprint to a newly created file named myrent-keys.txt.
- Store the file myrent-keys.txt in a secure location and ensure you maintain a backup version.
- Failure to retain a copy of the keys would mean that you would no longer be able to make updates to the myrent application.
- Failure to retain a copy of the keys would mean that you would no longer be able to make updates to the myrent application.
-
Register a Google account (or use an existing one) and sign in.
- Open the Google API Console
- Create a project named, for example, myrent (Figures 2 & 3).
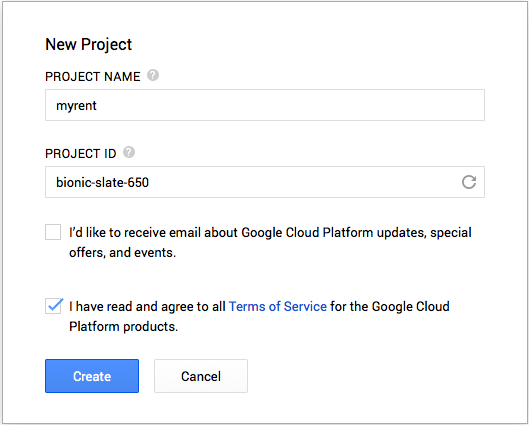
- Select Credentials in the Projects column and press the Create new key button (Figure 4).
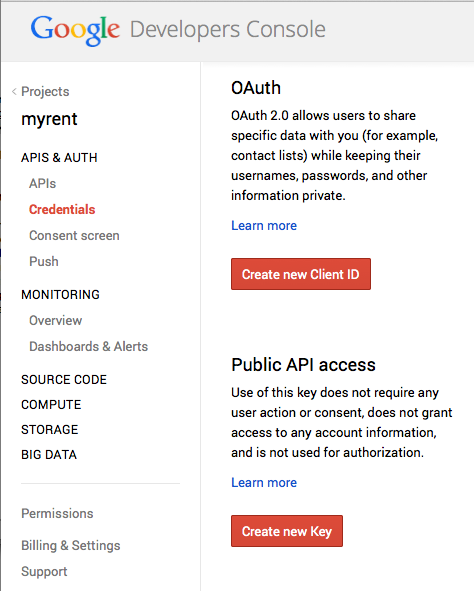
- The Create a new key window opens: press the Android key button (Figure 5).
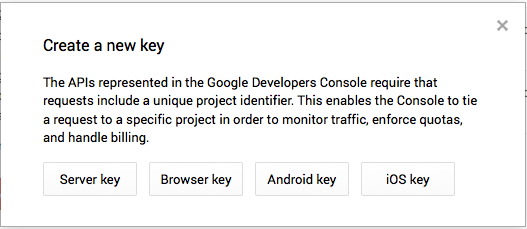
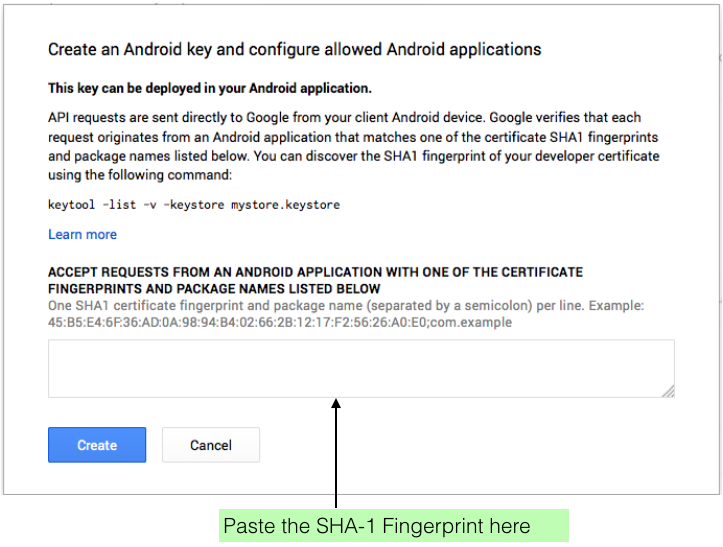
- A window similar to that illustrated in Figure 6 now opens:
- Paste the SHA-1 Fingerprint into the the area indicated, followed by a semi-colon, followed by the project package name.
- Example: 45:B8:A9:...DE;org.wit.myrent
- Press the Create button.
- A window showing the key and other relevant information should then appear as shown in Figure 7.
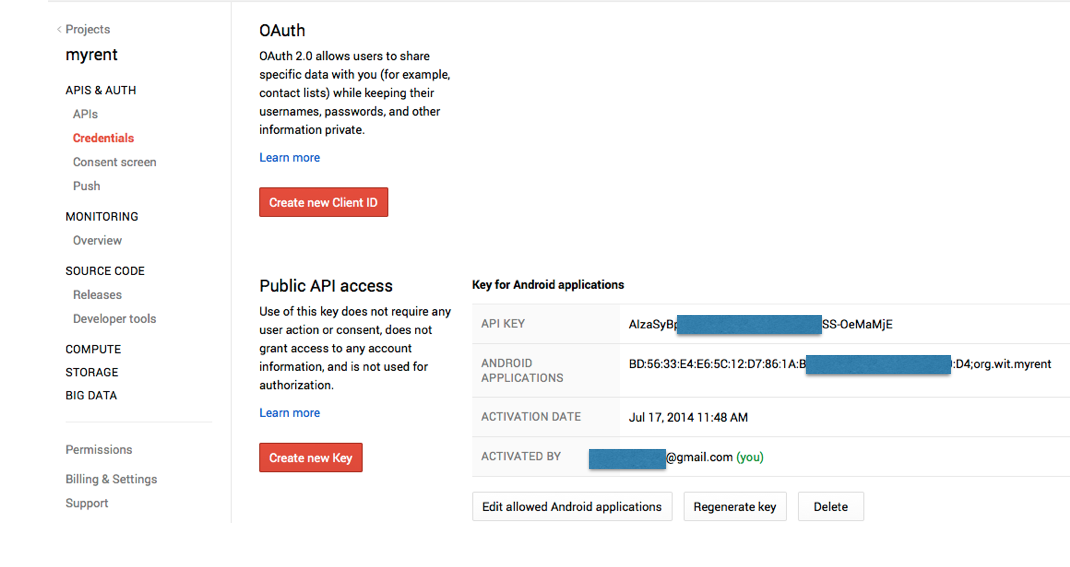
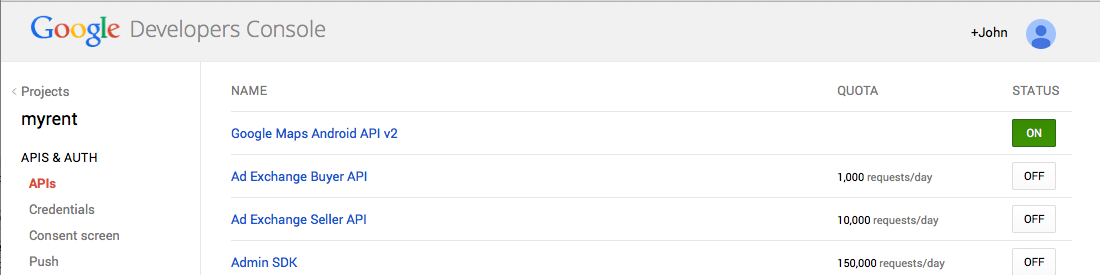
- Switch on Google Maps Android API v2
- Select APIS & AUTH and then APIs in the left-hand Projects column scroll to Google Maps Android API v2
- The button on the right should be off: if so, press it to turn it ON (Figure 8).
Here is a summary of the data that should be retained securely:
- The login | password pair for the Google account
- The SHA-1 fingerprint
- The API keys
Resources (Manifest)
In AndroidManifest.xml:
- Add GoogleMap permissions following the uses-sdk node:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<!-- The following two permissions are not required to use
Google Maps Android API v2, but are recommended. -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
- Immediately before the closing application tag add these metadata nodes:
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.maps.v2.API_KEY"
android:value="TODO: Insert your API key here" />
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version"/>
Replace the placeholder TODO: Inert your API key here with your key, created in an earlier step.
Verify that the Google Play Services library has been included by selecting the project name in Eclipse Package Explorer, right-click to open Properties window and then add google_play_services_lib as shown in Figure 1.
For reference here is the up-to-date manifest file:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="org.wit.myrent"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="16"
android:targetSdkVersion="19" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<!-- The following two permissions are not required to use
Google Maps Android API v2, but are recommended. -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
<application
android:name=".app.MyRentApp"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".activities.ResidenceListActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name=".activities.ResidencePagerActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<meta-data
android:name="android.support.PARENT_ACTIVITY"
android:value=".activities.ResidenceListActivity"/>
</activity>
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version"/>
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.maps.v2.API_KEY"
android:value="<TODO: Insert your API key here" />
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Resources (Layout)
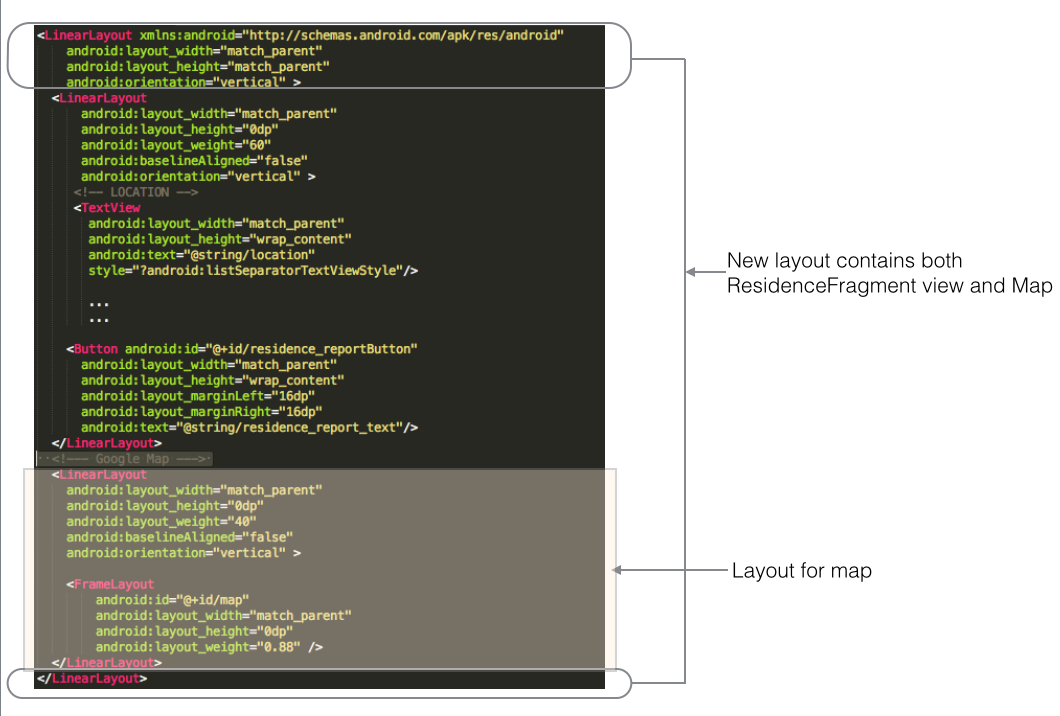
Refactor the layout of the detail view:

Filename: fragment_residence.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="60"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<!-- LOCATION -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/location"
style="?android:listSeparatorTextViewStyle"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:baselineAligned="false" >
<!-- Geolocation (GPS Coords) -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="60"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="@string/geolocation" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/geolocation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/geolocation_hint" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- Show Map Button -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="40"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/show_map"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:enabled="false" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- STATUS -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/status"
style="?android:listSeparatorTextViewStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/registration_date"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp" />
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/isrented"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:enabled="true"
android:focusable="false"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/rented_checkbox_text"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/tenant"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:text="@string/landlord" />
<Button android:id="@+id/residence_reportButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:text="@string/residence_report"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="40"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/map"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="0.88" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
Figure 2 should help you to understand the changes made here.
Model
Before we introduce the map code we shall modify the Residence model class allowing it to store the current zoom level of the map.
- The purpose is to ensure that the zoom level is retained as one switches between the list and detail views.
Here are the code snippets to be added to Residence.java:
//New fields
public double zoom ;//zoom level of accompanying map
private static final String JSON_ZOOM = "zoom" ; //map zoom level
Constructors:
public Residence()
{
...
zoom = 16.0f;
}
public Residence(JSONObject json) throws JSONException
{
...
zoom = json.getDouble(JSON_ZOOM);
}
toJSON method
public JSONObject toJSON() throws JSONException
{
...
json.put(JSON_ZOOM , zoom);
return json;
}
Helpers
Add this helper class to the org.wit.android.helpers package:
package org.wit.android.helpers;
import android.content.Context;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng;
public class MapHelper
{
public static LatLng latLng(Context context, String geolocation)
{
String[] g = geolocation.split(",");
if (g.length == 2)
{
return new LatLng(Double.parseDouble(g[0]), Double.parseDouble(g[1]));
}
return new LatLng(0, 0);
}
public static String latLng(LatLng geo)
{
return String.format("%.6f", geo.latitude) + ", " + String.format("%.6f", geo.longitude);
}
}
The method LatLng latLng(String geolocation) returns a LatLng object containing the latitude and longitude coordinates contained in the String geolocation.
The method String latLng(LatLng geo) returns a single string version of the coordinates contained in a LatLng object formed by concatenating the coordinates but separating them with a comma. For example:
52.253456,-7.187162
LatLng is a Google class representing a pair of latitude and longitude coordinates stored as degrees.
Please note that the use of a Context type as an argument above is not necessary at this time. We are including it here because it will be required later when we introduce validation and wish to generate Toast messages.
ResidenceFragment
Add imports
import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.CameraPosition;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment;
Add a method to initialize the map fragment:
private void initializeMapFragment()
{
FragmentManager fm = getChildFragmentManager();
mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) fm.findFragmentById(R.id.map);
if (mapFragment == null)
{
mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance();
fm.beginTransaction().replace(R.id.map, mapFragment).commit();
}
}
This fragment may be initialized only when the containing fragment has been created (ResidenceFragment).
- To do this we override onActivityCreated:
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
initializeMapFragment();
}
Disable mapButton and associated statements:
private Button mapButton;
mapButton = (Button) v.findViewById(R.id.show_map);
mapButton .setOnClickListener(this);
Add instance variables;
SupportMapFragment mapFragment;
GoogleMap gmap;
Marker marker;
LatLng markerPosition;
boolean markerDragged;
Note the boolean flag above (markerDragged).
- The flag is used to distinguish between geolocations input by the user and those generated by moving the marker.
We use the flag to avoid conflict that would otherwise arise as follows:
- The geolocation EditText control listens for any inputs by the user.
- When an input is detected the map immediately places a marker at this location and displays itself on the screen.
- If a user then drags the marker, representing a new geolocation, the code writes this new position to the EditText box.
- However, this change to the EditText box, without intervention, would trigger an unnecessary rendering of the map.
To avoid this potential cyclical behaviour, replace the afterTextChanged(Editable) method with the following:
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable c)
{
String thisGeolocation = c.toString();
Log.i(this.getClass().getSimpleName(), "geolocation " + thisGeolocation);
residence.geolocation = thisGeolocation;
getActivity().setTitle(thisGeolocation);
// using a flag, markerDragged, to avoid race condition
if (markerDragged == true)
{
markerDragged = false;
}
else
{
renderMap(MapHelper.latLng(getActivity(), thisGeolocation));
}
}
Change class signature to implement:
GoogleMap.OnMarkerDragListener
GoogleMap.OnCameraChangeListener
New signature is:
public class ResidenceFragment extends SupportMapFragment implements TextWatcher,
OnCheckedChangeListener,
OnClickListener,
DatePickerDialog.OnDateSetListener,
GoogleMap.OnMarkerDragListener,
GoogleMap.OnCameraChangeListener
This change necessitates implementation of associated interface methods which you may use QuickFix to resolve:
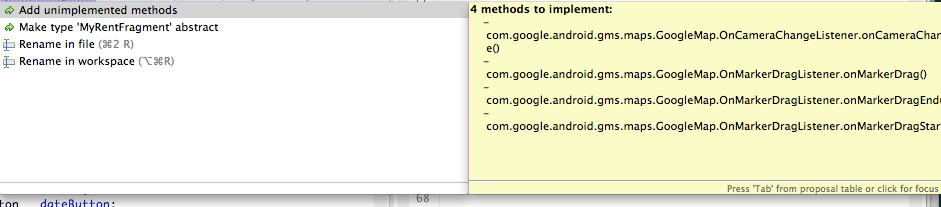
Here are the methods which we have, where applicable, fully implemented. First are the implementations of the OnMarkerDragListener interface:
@Override
public void onMarkerDrag(Marker arg0)
{
}
@Override
public void onMarkerDragEnd(Marker arg0)
{
residence.geolocation = MapHelper.latLng(arg0.getPosition());
getActivity().setTitle(residence.geolocation);
gmap.animateCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(arg0.getPosition()));
markerDragged = true;
}
@Override
public void onMarkerDragStart(Marker arg0)
{
}
Here is the implementation of the OnCameraChangeListener:
@Override
public void onCameraChange(CameraPosition arg0)
{
residence.zoom = arg0.zoom;
markerPosition = MapHelper.latLng(getActivity(), residence.geolocation);
if (marker != null)
{
marker.remove();
marker = null;
}
marker = gmap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(markerPosition).draggable(true).title("Residence").alpha(0.7f)
.snippet("GPS : " + markerPosition.toString()));
}
Next is the method to render the map:
private void renderMap(LatLng markerPosition)
{
if (mapFragment != null)
{
gmap = mapFragment.getMap();
if (gmap != null)
{
gmap.animateCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(markerPosition, (float) residence.zoom));
gmap.setMapType(GoogleMap.MAP_TYPE_HYBRID);
gmap.setOnMarkerDragListener(this);
gmap.setOnCameraChangeListener(this);
}
}
}
Next we override onStart() within which we invoke renderMap and register a listener to detect any changes to the map:
@Override
public void onStart()
{
super.onStart();
renderMap(MapHelper.latLng(getActivity(), residence.geolocation));
gmap.setOnCameraChangeListener(this);
}
Ensure that super is called in onCreateView:
super.onCreateView(inflater, parent, savedInstanceState);
Test the app as follows:
- Create a new residence and check the details view.
- Create a new residence and change the default geolocation.
- The marker and map should reflect the new geolocation.
- Change the zoom level, switch to the list view and back: the zoom level should be retained.
If you modify the geolocation such that the input becomes invalid then the app will crash. Here is example of invalid data:
We can solve this by introducing a try-catch block to MapHelper.latLng(Context, String) as follows:
package org.wit.android.helpers;
import android.content.Context;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng;
import java.lang.NumberFormatException;
import static org.wit.android.helpers.LogHelpers.info;
public class MapHelper
{
public static LatLng latLng(Context context, String geolocation)
{
String[] g = geolocation.split(",");
try
{
if (g.length == 2)
{
return new LatLng(Double.parseDouble(g[0]), Double.parseDouble(g[1]));
}
}
catch (NumberFormatException e)
{
info(context, "Number format exception: invalid geolocation: " + e.getMessage());
}
Toast.makeText(context, "An invalid geolocation has been entered: defaulting to 0,0", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return new LatLng(0, 0);
}
public static String latLng(LatLng geo)
{
return String.format("%.6f", geo.latitude) + ", " + String.format("%.6f", geo.longitude);
}
}
Add these import statements:
import java.lang.NumberFormatException;
import android.widget.Toast;
Test this validation as follows:
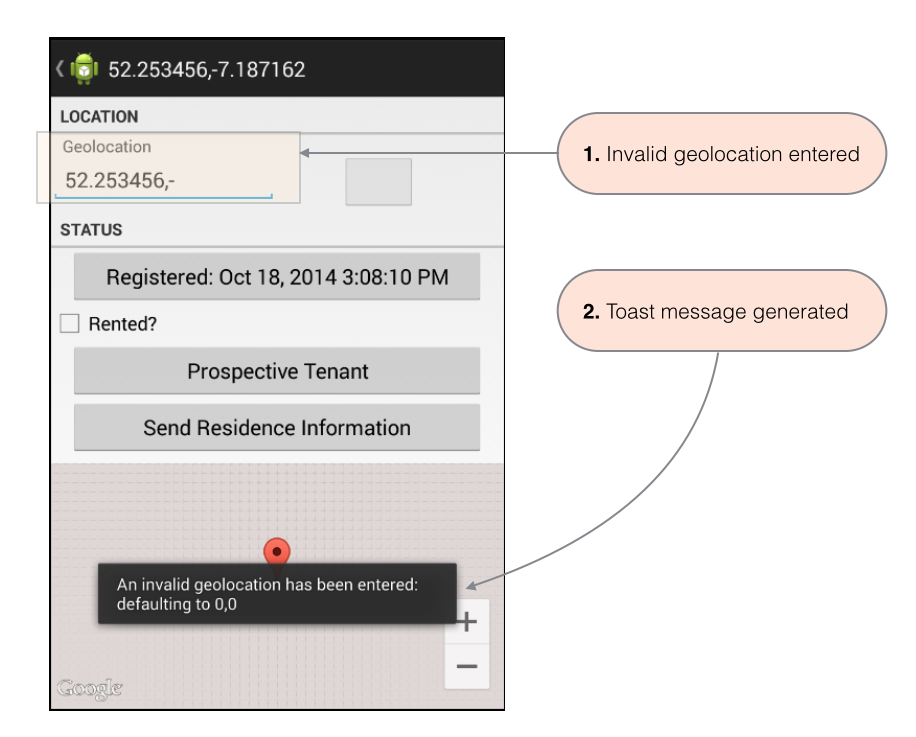
- Continue deleting digits from the default geolocation until the data is invalid as shown in Figure 1 above.
- This will result in Toast messages being generated as shown in Figure 2.
- Once you correct the input these messages are no longer generated and the map should automatically render correctly.
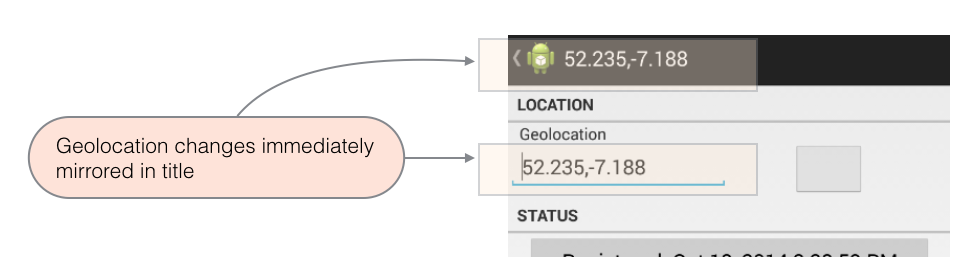
The final task in this step is to immediately mirror the geolocation in the title as the input is changed (as shown in Figure 3).
- To do this, refactor the method *onMarkerDragEnd.
Simply add the following line of code at the end of onMarkerDragEnd.
geolocation.setText(residence.geolocation);
Run the app and test the features added above namely those that ensure that:
- A map is rendered
- Inputting invalid data generates a Toast message
- Inputting valid data following the toast message results in the map rendering correctly
- The title immediately mirrors any changes in the geolocation input.
- The EditText input box display changes dynamically as the marker is dragged.
Scrollable (portrait)
Make the data-input portion of the details view scrollable.
Official documentation on ScrollView is available here:

Here is the refactoted fragment_residence.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="60"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/container"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!-- LOCATION -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/location"
style="?android:listSeparatorTextViewStyle"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:baselineAligned="false" >
<!-- Geolocation (GPS Coords) -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="60"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="@string/geolocation" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/geolocation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/geolocation_hint" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- Show Map Button -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="40"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/show_map"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:enabled="false" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- STATUS -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/status"
style="?android:listSeparatorTextViewStyle"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/registration_date"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp" />
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/isrented"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:enabled="true"
android:focusable="false"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/rented_checkbox_text"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/tenant"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:text="@string/landlord" />
<Button android:id="@+id/residence_reportButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:text="@string/residence_report"/>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="40"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/map"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
Replace the existing code with above and test that the details view is now scrollable:
- Note that the map section is not scrollable.
- Note also that the introduction of this change may result in the soft keyboard being automatically opened when the app is installed on a physical device.
- To avoid this occurrence modify the ResidencePagerActivity in the Manifest file as follows:
<activity
android:name=".activities.ResidencePagerActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:windowSoftInputMode="stateHidden|adjustResize" >
Figure 1 should help you to understand the changes made here.

Landscape
We shall now add a landscape layout.
- Create a new folder: res/layout-land.
- Add the following fragment_residence.xml file to this folder.
- Build and install the app on a device and check that the details view renders satisfactorily in both portrait and landscape modes.
- Study the landscape and portrait files and note small number of changes made to the portrait version to make it suitable for landscape.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" android:baselineAligned="false">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="60"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/container"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!-- LOCATION -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/location"
style="?android:listSeparatorTextViewStyle"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:baselineAligned="false">
<!-- Geolocation (GPS Coords) -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="60"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="@string/geolocation" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/geolocation"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/geolocation_hint" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- Show Map Button -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="40"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/show_map"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:enabled="false" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<!-- STATUS -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/status"
style="?android:listSeparatorTextViewStyle"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/registration_date"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/isrented"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:enabled="true"
android:focusable="false"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/rented_checkbox_text"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/tenant"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:text="@string/landlord" />
<Button android:id="@+id/residence_reportButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:text="@string/residence_report"/>
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="40"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/map"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
Test the scrollable feature in both portrait and landscape modes.
- It may be necessary to do so on a physical device (phone) as the scrollable feature is only evident when the screen size demands it.