World
color.h
#pragma once
struct Color
{
float R;
float G;
float B;
float A;
static Color White;
static Color Yellow;
static Color Red;
static Color Magenta;
static Color Cyan;
static Color Green;
static Color Black;
static Color Blue;
Color();
Color(float r, float g, float b, float a=1.0f);
Color(int r, int g, int b, int a=255);
void render();
void renderClear();
};
color.cpp
#include "libopengl.h"
#include "Color.h"
Color Color::Black (0, 0, 0);
Color Color::Blue (0, 0, 255);
Color Color::Green (0, 255, 0);
Color Color::Cyan (0, 255, 255);
Color Color::Red (255, 0, 0);
Color Color::Magenta (255, 0, 255);
Color Color::Yellow (255, 255, 0);
Color Color::White (255, 255, 255);
Color::Color()
{
R = G = B = A = 1.0f;
}
Color::Color(float r, float g, float b, float a)
{
R = r;
G = g;
B = b;
A = a;
}
Color::Color(int r, int g, int b, int a)
{
R = (float) r / 255.0f;
G = (float) g / 255.0f;
B = (float) b / 255.0f;
A = (float) a / 255.0f;
}
void Color::render()
{
glColor4f(R,G,B,A);
}
void Color::renderClear()
{
glClearColor(R,G,B, 1.0f);
}
vector3.h
#pragma once
#include <istream>
struct Vector3
{
float X;
float Y;
float Z;
static Vector3 UnitX;
static Vector3 UnitY;
static Vector3 UnitZ;
Vector3(float x, float y, float z);
Vector3(float value);
Vector3();
Vector3(std::istream& is);
void translate();
void rotate (float angle);
void render();
};
vector3.cpp
#include "libopengl.h"
#include "vector3.h"
using namespace std;
Vector3 Vector3::UnitX(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Vector3 Vector3::UnitY(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
Vector3 Vector3::UnitZ(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
Vector3::Vector3(float x, float y, float z)
: X(x)
, Y(y)
, Z(z)
{}
Vector3::Vector3(float value)
: X(value)
, Y(value)
, Z(value)
{}
Vector3::Vector3()
: X(0)
, Y(0)
, Z(0)
{}
Vector3::Vector3(istream &is)
{
is >> X >> Y >> Z;
}
void Vector3::render()
{
glVertex3f(X, Y, Z);
}
void Vector3::translate()
{
glTranslatef(X,Y,Z);
}
void Vector3::rotate (float angle)
{
glRotatef(angle, X,Y,Z);
}
world.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#define theWorld World::GetInstance()
class World
{
public:
static World& GetInstance();
void setCmdlineParams(int*argc, char **argv);
void initialize(int width, int height, std::string name);
void start();
void render();
void keyPress(unsigned char ch);
private:
static World* s_World;
int *argc;
char **argv;
};
world.cpp
#include "world.h"
#include "libopengl.h"
#include "vector3.h"
#include "color.h"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
World* World::s_World = NULL;
void reshape(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei) w, (GLsizei) h); //set the viewportto the current window specifications
glMatrixMode ( GL_PROJECTION); //set the matrix to projection
glLoadIdentity();
gluPerspective(60, (GLfloat) w / (GLfloat) h, 1.0, 1000.0); //set the perspective (angle of sight, width, height, ,depth)
glMatrixMode ( GL_MODELVIEW); //set the matrix back to model
}
void renderScene(void)
{
World::GetInstance().render();
}
void keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
{
World::GetInstance().keyPress(key);
}
World& World::GetInstance()
{
if (s_World == NULL)
{
s_World = new World();
}
return *s_World;
}
void World::setCmdlineParams(int*argc, char **argv)
{
this->argc = argc;
this->argv = argv;
}
void World::render()
{
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glLoadIdentity();
glutSwapBuffers();
}
void World::keyPress(unsigned char ch)
{
glutPostRedisplay();
}
void World::initialize(int width, int height, std::string name)
{
glutInit(argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH);
glutInitWindowSize(width, height);
glutCreateWindow(name.c_str());
Color::Black.renderClear();
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glFrontFace(GL_CCW);
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT,GL_LINE);
glPolygonMode(GL_BACK,GL_LINE);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluPerspective(60.0f, 1, 1.0, 1000.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
//glTranslatef(0.0f, 0.0f, -200.0f);
glutKeyboardFunc(keyboard);
glutReshapeFunc(reshape);
glutDisplayFunc(renderScene);
}
void World::start()
{
glutMainLoop();
}
main.cpp
#include "world.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
theWorld.setCmdlineParams(&argc, argv);
theWorld.initialize(800,600, "First World");
theWorld.start();
return 0;
}
World+Model
- Introduce a model as a private member of the world class:
Model theModel;
- Along with a public member to load the model:
void loadModel (std::string modelName);
- And we can now implement this load member:
void World::loadModel (std::string modelName)
{
ifstream inStream;
inStream.open(modelName.c_str(), ios::in);
if (##inStream.fail())
{
theModel.load(inStream);
}
}
- and in World::render() - would should now call render on the model:
void World::render()
{
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glLoadIdentity();
theModel.render();
glutSwapBuffers();
}
- Finally, we can go back to main and load our model:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
theWorld.setCmdlineParams(&argc, argv);
theWorld.initialize(800,600, "First World");
theWorld.loadModel("cube.obj");
theWorld.start();
return 0;
}
The program should output to the console something like this:
rendering default with 0 faces
rendering pCube1 with 7 faces
1 1 1
2 2 2
4 4 4
3 3 3
3 3 3
4 4 4
6 6 6
5 5 5
5 5 5
6 6 6
8 8 8
7 7 7
7 7 7
8 8 8
2 2 2
1 1 1
2 2 2
8 8 8
6 6 6
4 4 4
7 7 7
1 1 1
3 3 3
5 5 5
7 7 7
1 1 1
3 3 3
5 5 5
Rendering
- We can now see if we are getting the right vertices rendered. Change faces::render as follows:
void Face::render(std::vector <Vector3>&defaultTable)
{
for (int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
cout << defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].X << " " << defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].Y << " " << defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].Z << endl;
}
}
- Which, when executed, should render:
rendering default with 0faces
rendering pCube1 with 7faces
-5.25187 0 0.717793
3.83551 0 0.717793
3.83551 2.49571 0.717793
-5.25187 2.49571 0.717793
-5.25187 2.49571 0.717793
3.83551 2.49571 0.717793
3.83551 2.49571 -2.09405
-5.25187 2.49571 -2.09405
-5.25187 2.49571 -2.09405
3.83551 2.49571 -2.09405
3.83551 0 -2.09405
-5.25187 0 -2.09405
-5.25187 0 -2.09405
3.83551 0 -2.09405
3.83551 0 0.717793
-5.25187 0 0.717793
3.83551 0 0.717793
3.83551 0 -2.09405
3.83551 2.49571 -2.09405
3.83551 2.49571 0.717793
-5.25187 0 -2.09405
-5.25187 0 0.717793
-5.25187 2.49571 0.717793
-5.25187 2.49571 -2.09405
-5.25187 0 -2.09405
-5.25187 0 0.717793
-5.25187 2.49571 0.717793
-5.25187 2.49571 -2.09405
- Getting this onto our screen is easy. Extend the above function to render QUADS:
void Face::render(std::vector <Vector3>&defaultTable)
{
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
glVertex3f( defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].X,
defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].Y,
defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].Z );
cout << defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].X << " " << defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].Y << " " << defaultTable[vertices[i] - 1].Z << endl;
}
glEnd();
}

- As we are using perspective projection, our eye co-ordinates are at the origin. So, in World::render(), move the world back 10 units:
void World::render()
{
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glLoadIdentity();
Vector3(0,0,-10).translate();
theModel.render();
glutSwapBuffers();
}
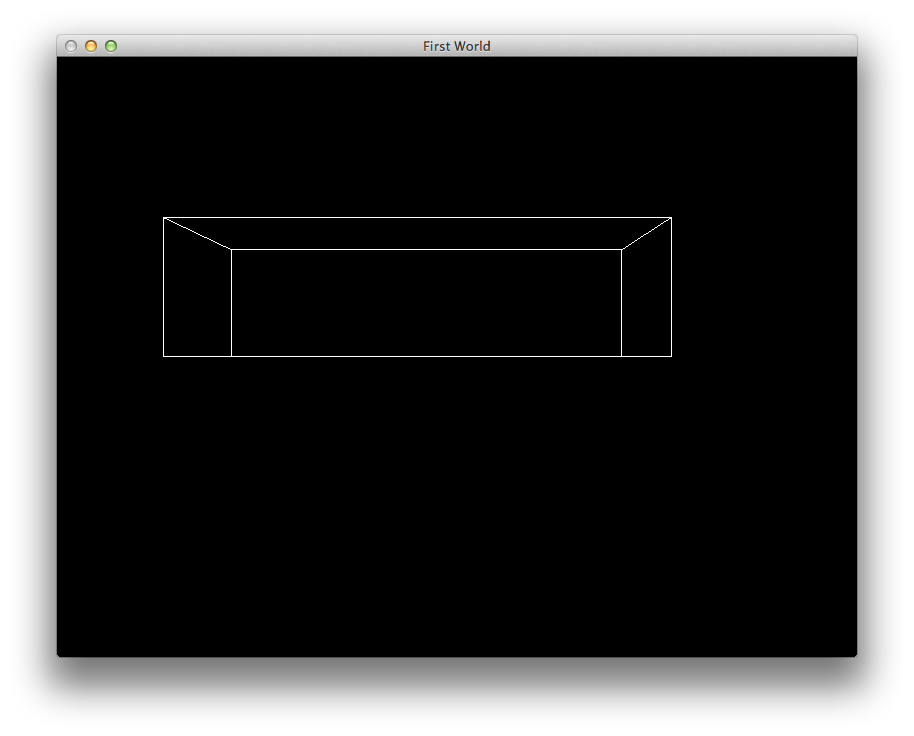
- Which should let is see the cube: